Nureva Console uses the default port 8931 for the WebSocket server with camera integrations. This port is configurable in Nureva Console and can be set to any port number. Depending on the network and security setup, some unused and open ports can be blocked at the network, computer or router level.
Nureva Console client and the camera software may need to be allowed to make connections and share sound location data using the default port or any other port. Enabling a network port on both a router and a computer involves several steps. The exact process can vary depending on the router and the computer's operating system, but here's a general outline of the steps you might need to take.
Step 1: Identify the network port the third-party camera requires or select a specific port.
The first step is to identify the network port the third-party camera requires. This information can be found in the camera's documentation. The default and most common port used by IP cameras is port 8931.
Step 2: Check if the port is open.
Step 3: Enable the required network port on the router or PC.
Once you've identified the required network port and protocol (TCP or UDP), if not open, you must enable it on the router or PC, depending on the level at which it's blocked.
Step 4: Add the allowed hostnames.
The final step is to add the allowed host names to Nureva Console. This will allow Nureva Console to communicate with the third-party camera. The allowed hostnames are the IP addresses or hostnames of the cameras that you want to integrate with Nureva Console.
Open Nureva Console and go to Settings > Integrations > Local Integrations to add the allowed hostnames. Enter the IP address or hostname of the camera. Click the Save button to save your changes.
Once you've completed these steps, the third-party cameras will be able to communicate with Nureva Console and can be used for camera tracking.
NOTE: While you may be able to allow ports on your local machine, we recommend getting support from your IT team to open any port on your router to ensure you enable only the ports required by the third-party camera. Enabling unnecessary ports can increase your security risk.
Check if a network port is open
Windows®
There are a few ways to check if a network port is open. Below are two easy options.
Option 1:
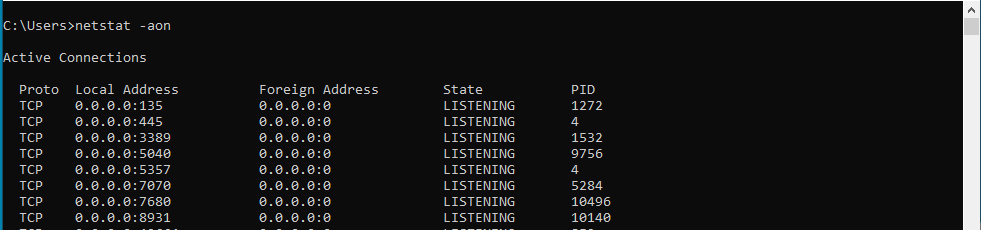
- Open the command prompt by pressing the Windows key + R and typing "cmd"
- Type "netstat -aon" and press Enter
- Look for the port numbers in the LISTENING state
- These are the ports you'll need to have open for streaming
- If the port numbers aren't in the LISTENING state, you'll need to open them manually
Option 2:
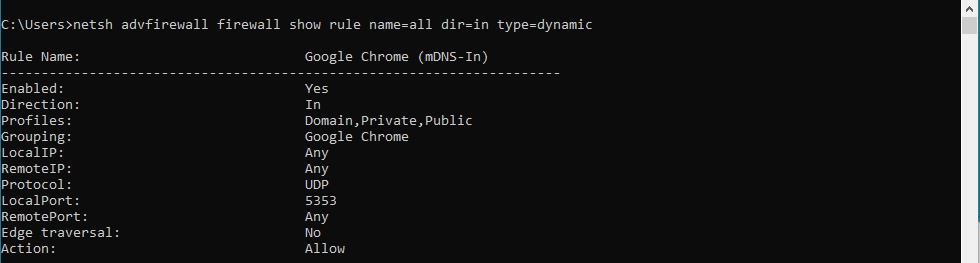
- Open the command prompt by pressing the Windows key + R and typing "cmd"
- Type "netsh advfirewall firewall show rule name=all dir=in type=dynamic"
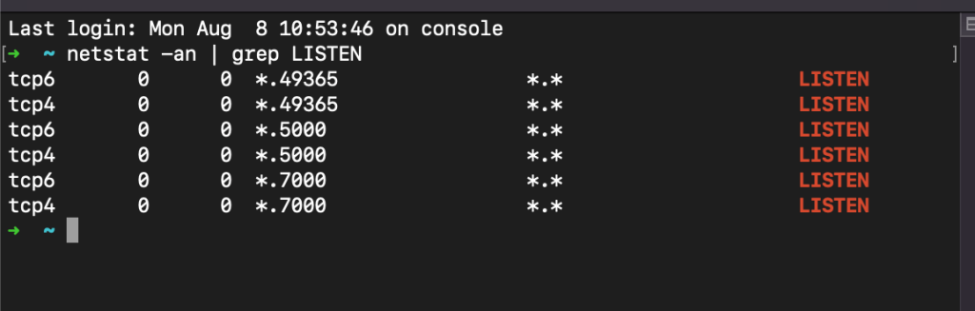
- Open the Terminal application and type "netstat -an | grep LISTEN"
- This will show you a list of all the open ports on your Mac®, along with the process ID verification service (PID) and name of the application that’s using each port
- If you’re unsure about what a particular port is used for, you can look it up in the "/etc/services" file
- To view the contents of this file, type "cat /etc/services"
 Delete
Delete
Enabling a network port on a router or computer
Enabling a network port on a router
The steps below for allowing a port vary depending on the type of router you have. You will need to find the port forwarding section in the router's settings and add a rule for the port you want to allow. The rule should specify the internal IP address of the camera and the external port number.
Access router settings: Open a web browser on a device connected to the same network as the router. Enter the router's IP address in the address bar. The default IP address is often "192.168.1.1" or "192.168.0.1". You'll need to enter the router's admin username and password.
Navigate to port forwarding: The exact location of this option can vary depending on the router's interface. Look for "Port Forwarding," "Port Mapping," or "Virtual Server" options. This is where you'll specify which external ports should be forwarded to internal devices.
Add a port forwarding rule: You'll need to add a new rule in the port forwarding section. This usually involves specifying the protocol (TCP or UDP), the external port, the internal IP address of the PC and the internal port you want to forward to. This tells the router to send incoming data on the specified external port to the internal PC's IP address and port.
Save settings: After adding the port forwarding rule, be sure to save the settings. The router will now start directing incoming traffic on the specified port to your PC.
Enabling a network port on a computer
Windows®
Windows (as with many other operating systems) includes a built-in firewall that regulates incoming and outgoing network traffic. If the firewall is blocking the port you want to enable, you'll need to create an exception.
Access Windows firewall settings
You can access the firewall settings using the easy options below.
Option 1:
- Press Windows key+S together
- Type "Windows Defender Firewall"
- Click on Windows Defender Firewall
Option 2:
- Press Windows + R to open the Run dialog
- Type "Control Panel" and click OK
- Select "Windows Defender Firewall"
Create an inbound rule
In the firewall settings, you must create an inbound rule to allow traffic to the specific port.
- Click on "Advanced settings" or "Advanced firewall settings"
- In the left pane, select "Inbound Rules"
- Click on "New Rule..." in the right pane
- Choose "Port" as the rule type and click Next

- Select "TCP" or "UDP" depending on the protocol used by the application
- Select "Specific local ports" and enter the port number you want to enable
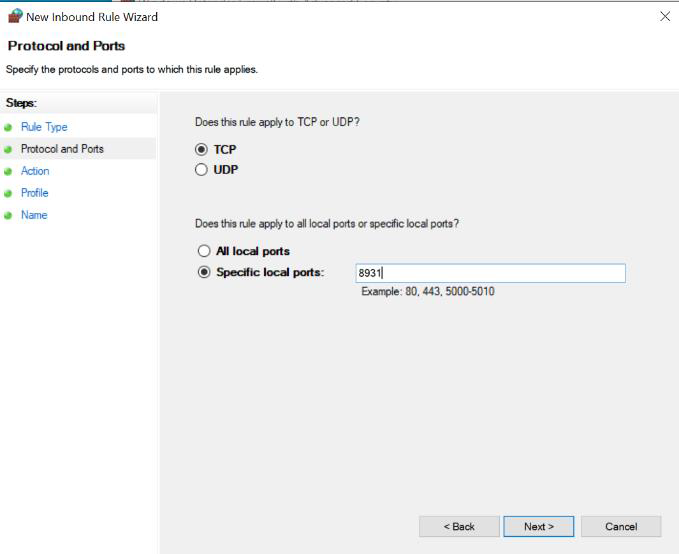
- Choose "Allow the connection" and click Next
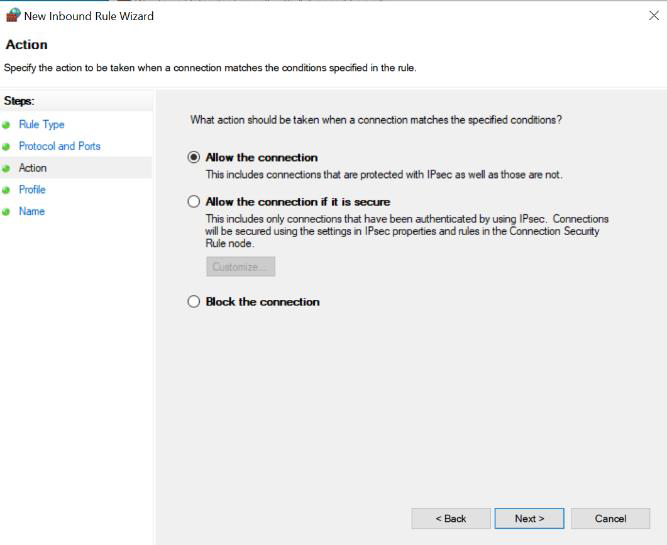
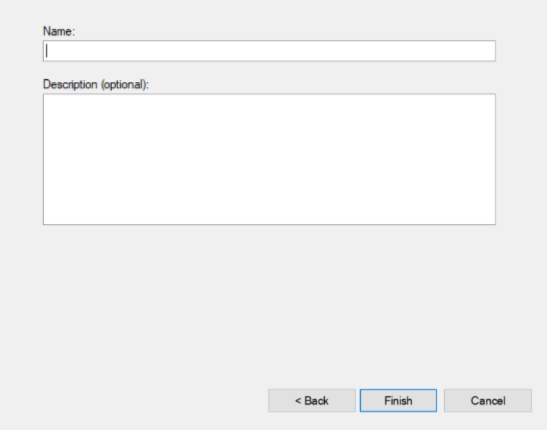
- Provide a name for the rule and an optional description
- Click Finish to create the rule
After the inbound rule, it should take effect immediately. However, if you're still facing issues, you might need to restart your computer or the network services you're working with.
Test the port
Once you've set up port forwarding on the router and configured your PC, you can test the port to see if it's open and accessible from the outside.
macOS®
The macOS firewall, by default, is disabled. That means your computer will accept all incoming and outgoing connections. But if you've turned on the firewall, you might need to open a port to allow an inbound connection as follows.
- Go to the Terminal app
- Type "sudo pfctl -d" to stop the filter firewall
- Now enter "sudo nano /etc/pf.conf"
- Go to the end of all configurations
- Type "pass in inet proto tcp from any to any port [add port number] no state"
- This roughly translates to allowing incoming TCP from any machine to any other machine on that specific port number without inspection
- Hold down Ctrl+X together to exit the nano
- Press "Y" and press Enter
NOTE: The technical information provided in this article, including specifications and recommendations, is provided for customer convenience. The accuracy of this information is not guaranteed and is subject to change without notice. Please check the user manuals and related documentation from each product manufacturer to ensure that your setup meets the proper recommendations.